Abstract
BACKGROUND: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) mutations are found in about 10-15% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases. Enasidenib (ENA) is a first‐in‐class mutant IDH2 inhibitor that induces differentiation of IDH2-mutated leukemic cells. However, the clinical efficacy of single agent ENA therapy in relapsed or refractory (R/R) AML is limited, underscoring the need for combination therapy. Preclinical studies have shown that IDH-mutated leukemic cells are particularly sensitive to BCL2 inhibition with venetoclax (VEN), a finding supported by clinical studies of VEN combination therapies. We previously demonstrated that the combination of ENA and VEN can be more effective than each drug alone, in reducing leukemic burden in patient-derived xenograft models of IDH2-mutated AML. Here, we report preliminary safety and efficacy results of an ongoing open-label, single-arm, phase Ib/II trial (NCT04092179) of ENA in combination with VEN in patients with IDH2-mutated myeloid malignancies.
METHODS: Patients 18 years of age or above with IDH2-mutated R/R AML or high-risk MDS/MPN and an ECOG performance status of 0-2 were eligible. Patients previously treated with an IDH2 or BCL2 inhibitor were excluded. Participants received VEN continuously starting on cycle 1 day 1 with a 3-day ramp-up to a target dose of 400 mg daily (dose level 0) in cohorts 1 and 2. ENA was administered at 100 mg daily continuously starting on cycle 1 day 15. Each cycle was 28 days. Concurrent use of a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor was allowed with 50% dose reduction of VEN after completion of the first 2 cycles at 100% target dose. Interruptions of VEN and/or ENA were permitted for management of adverse events (AEs). Primary endpoints were 1) safety and tolerability and 2) overall response rate (ORR) defined as complete remission (CR) + CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) + morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS) + partial remission (PR) by revised IWG criteria. Secondary endpoints include pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles of VEN, duration of response, overall survival (OS), and IDH2 mutant allele burden in bone marrow by ddPCR.
RESULTS: The study opened to recruitment in November of 2020. As of July 28, 2021 (data cutoff), 11 patients were enrolled on study; 10 with R/R AML and 1 with very-high risk MDS by IPSS-R. Six patients had a R140Q mutation, and 5 had a R172K mutation. Median age was 72 years (range: 32 - 80); 6 patients were male. Participants had received a median of 2 prior lines of therapies (range: 1 - 4). Six of 10 AML patients had primary refractory disease. The MDS patient experienced secondary azacitidine failure.
Key treatment emergent grade ≥ 3 AEs regardless of attribution were: febrile neutropenia (n=3), intracranial hemorrhage (n=3), lung infection (n=2), other infection (n=2), elevated AST/ALT (n=2), sepsis (n=1), leukocytosis (n=1), TRALI (n=1), and small bowel obstruction (n=1). No cases of differentiation or tumor lysis syndrome were observed. No patients discontinued the study due to AEs. The addition of ENA, a known inhibitor of CYP3A4, did not significantly affect the PK profiles of VEN.
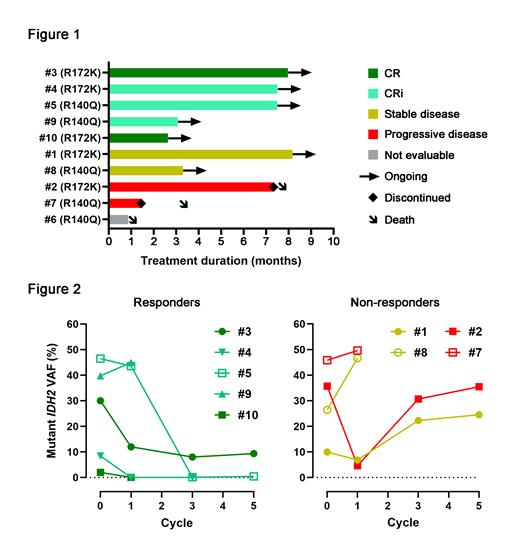
Nine of the AML patients completed at least 1 cycle of treatment and are considered evaluable for efficacy. One AML patient died from intracranial hemorrhage prior to completion of cycle 1. Median duration of observation is 3.5 months. Of the evaluable patients, CR was achieved in 2 patients (22%) and CRi in 3 patients (33%) for an ORR of 55% (Fig. 1). Median number of cycles to response was 3. All responders remain in remission and on study with a median of 6 cycles received to date (range: 3 - 8). Of the remaining 4 patients, 2 patients (22%) remain on study with stable disease, and 2 patients (22%) experienced progressive disease and died (one after 7 cycles and the other after 1 cycle). Median OS for the entire cohort has not been reached. A sustained reduction in mutant IDH2 allele frequency in bone marrow correlated with response (Fig. 2). For the MDS patient, no response was observed after 1 cycle of treatment.
CONCLUSIONS: VEN in combination with ENA is a well-tolerated regimen with no dose-limiting toxicities observed at the current dose level. The preliminary efficacy of this combination is encouraging with an ORR of 55% in evaluable R/R AML patients, with some responders achieving deep molecular remissions. Patient enrollment in dose-escalation cohorts is ongoing.
Chan: AbbVie: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Gupta: Sierra Oncology: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Constellation Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy; BMS-Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy. Maze: Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene-BMS: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; PharmaEssentia: Research Funding; Kronos Bio: Research Funding. Minden: Astellas: Consultancy. Schimmer: Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Medivir AB: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria; UHN: Patents & Royalties. Schuh: AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astellas: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; GlycoMimetics: Research Funding; Kite/Gilead: Research Funding; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Teva: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Yee: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Forma Therapeutics: Research Funding; F. Hoffmann La Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Tolero: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Shattuck Labs: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Onconova: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Otsuka: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Paladin: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Geron: Research Funding; MedImmune: Research Funding; Jazz: Research Funding; TaiHo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria; Astex: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. DiNardo: Agios/Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Notable Labs: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Foghorn: Honoraria, Research Funding; Forma: Honoraria, Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; ImmuneOnc: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb company: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Enasidenib is approved for the treatment of relapsed or refractory AML as single agent. Venetoclax, in combination with azacitidine or low-dose cytarabine, is approved for the treatment of newly diagnosed AML patients who are 75 years or older, or who have comorbidities that preclude use of intensive induction chemotherapy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal